As discussed in Chapter I/1.2.2 Contact Springs, the three basic requirements for the contact spring are:
• Electrical conductivity
• Creating the contact normal force
• Formability sufficient for both separable and permanent connections
Consider each requirement separately.
Electrical Conductivity
The contact spring material must have a high electrical conductivity. In general this means metallic conductivity. The conductivity of a contact spring depends on the intrinsic conductivity of the spring material and the geometry of the contact spring. The conductivity requirement is most demanding in power applications where Joule, I2 R, heating can limit the range of application of a connector.
Contact Force
The contact force is created by deflection of the contact springs, usually the receptacle contact spring, during mating of the connector. Material parameters that are important in generating the contact force include the elastic modulus, and the yield strength of the spring material. Examples of this dependence will be provided later in this chapter.
Formability
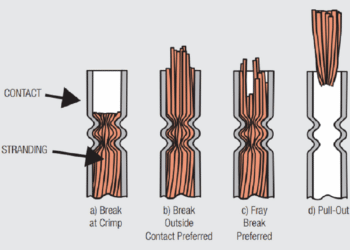
Formability is important for both separable and permanent connections. First, it is necessary to enable the various bending operations required to create the overall geometry of the separable connection portion of the contact spring. These geometries range from simple cantilever beams to complex curvatures to meet different application requirements. Second, it is necessary to support the large deformations and deflections needed for crimped connections as well as for insulation displacement connection geometries
As mentioned in Chapter I/1.2.2 Contact Springs, these contact spring material requirements are best met by copper alloys. Copper itself excels in conductivity, but it does not have the balance of strength and formability to meet the required contact spring manufacturing and performance requirements. Thus, a range of copper alloys are used with the choice of alloy being dependent on the connector design and the performance requirements that must be met. For example, for springs requiring complex forming the balance between yield strength and formability may be dominant while in power applications electrical conductivity may drive the material selection process.